What is light?
A form of energy that brightly illuminates the world we live in is called light.
Various electromagnetic waves, including visible light, are emitted from hot objects or objects with energy.
Visible light is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that the human eye can see.
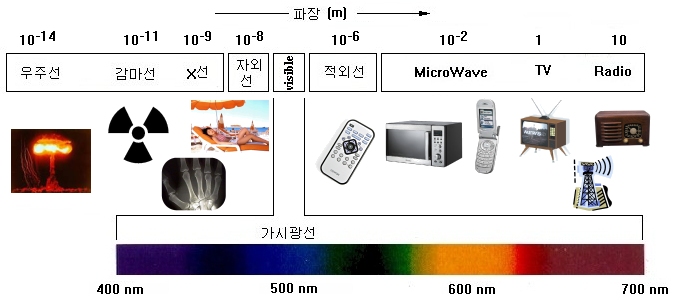
Types of electromagnetic waves
Electromagnetic waves are classified based on the length of the wavelength. Wavelength is the length of the entire wave until the same phase repeats itself.
It is said that the most efficient antenna length used in wireless communication is 1/2 of the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave.
The emitted light energy increases as the wavelength decreases.
c: speed of light (3×108m/s)
λ: wavelength (m)
υ: frequency (Hz)
Electromagnetic waves run at a speed of 300,000 km/s in a vacuum. Nothing is faster than Electromagnetic waves in this world.
- Gamma rays: 50 fm / 6 ×1021 Hz / 25 MeV (typical wavelength / frequency / photon energy)
- X-ray: 50 pm / 6 ×1018 Hz / 25 keV
- Ultraviolet rays: 100 nm / 3 ×1015 Hz / 12 eV
- Visible light: 550 nm / 5 ×1014 Hz / 2 eV
- Infrared: 10 μm / 3 ×1013 Hz / 120 meV
- Microwave: 1 cm / 3 ×1010 Hz / 120 μeV
- Radio wave: 1 km / 3 ×105 Hz / 1.2 neV